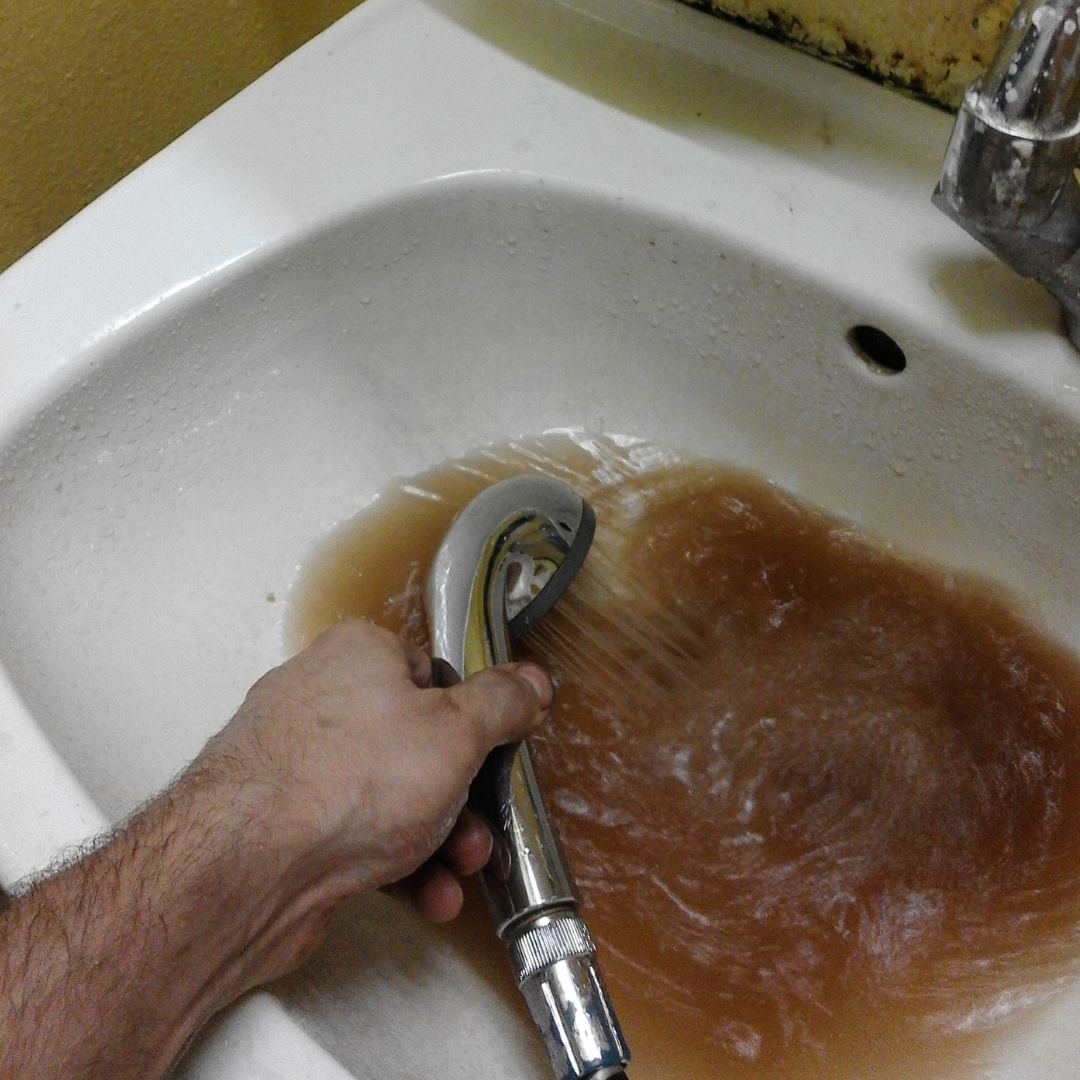
AUDITOR GENERAL REPORT ON CLEAN WATER IN FIRST NATIONS Prime Minister Justin Trudeau had no problem finding $7 billion dollars to buy Trans Mountain oil pipelines – so, where’s the money to pay for clean water pipelines in Indigenous communities? It may be hard to believe, but many First Nations in Canada still lack access…
Continue reading…about Canada Fails Again: First Nation Communities Without Clean Water